A television (TV) is an electronic device used to receive and display visual and audio content. It works by converting broadcast signals, cable input, or streaming data into images and sounds. TVs have evolved significantly from bulky cathode ray tube (CRT) models to modern flat-panel displays like LCD, LED, OLED, and QLED.
Types of TVs:
◆ CRT (Cathode Ray Tube):
- Bulky and heavy with curved screens.
- Uses electron beams to create images.
◆ Plasma:
- Older technology that uses gas-filled cells.
- Great color and contrast but bulky and prone to burn-in.
◆ LCD (Liquid Crystal Display):
- Flat, lightweight, and energy-efficient.
- Uses liquid crystals illuminated by backlights.
◆ LED (Light Emitting Diode):
- Advanced version of LCD with LED backlighting.
- Offers better contrast and energy efficiency.
◆ OLED (Organic LED):
- Self-illuminating pixels, no backlight required.
- Superior contrast, color accuracy, and thin design.
◆ QLED (Quantum Dot LED):
- Uses quantum dots for improved brightness and color.
- Competes with OLED in picture quality.
TV Internal Parts:
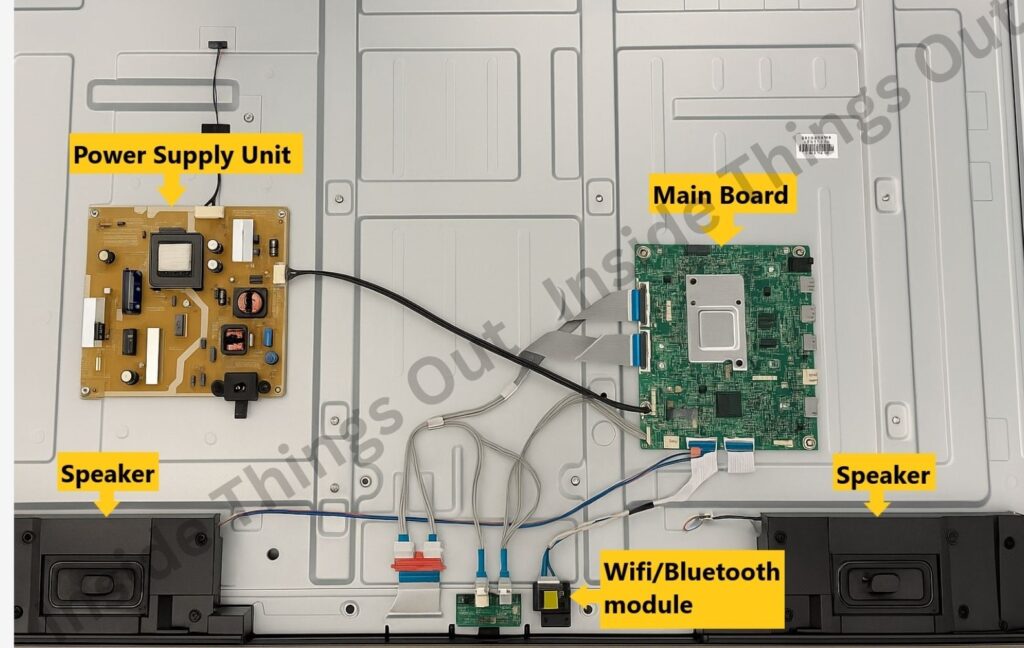
➢ Power Supply Board:
The power supply board takes the AC voltage from your outlet and converts it to various DC voltages needed to power everything else in your TV. It contains various electronic components. Please find mentioned below:
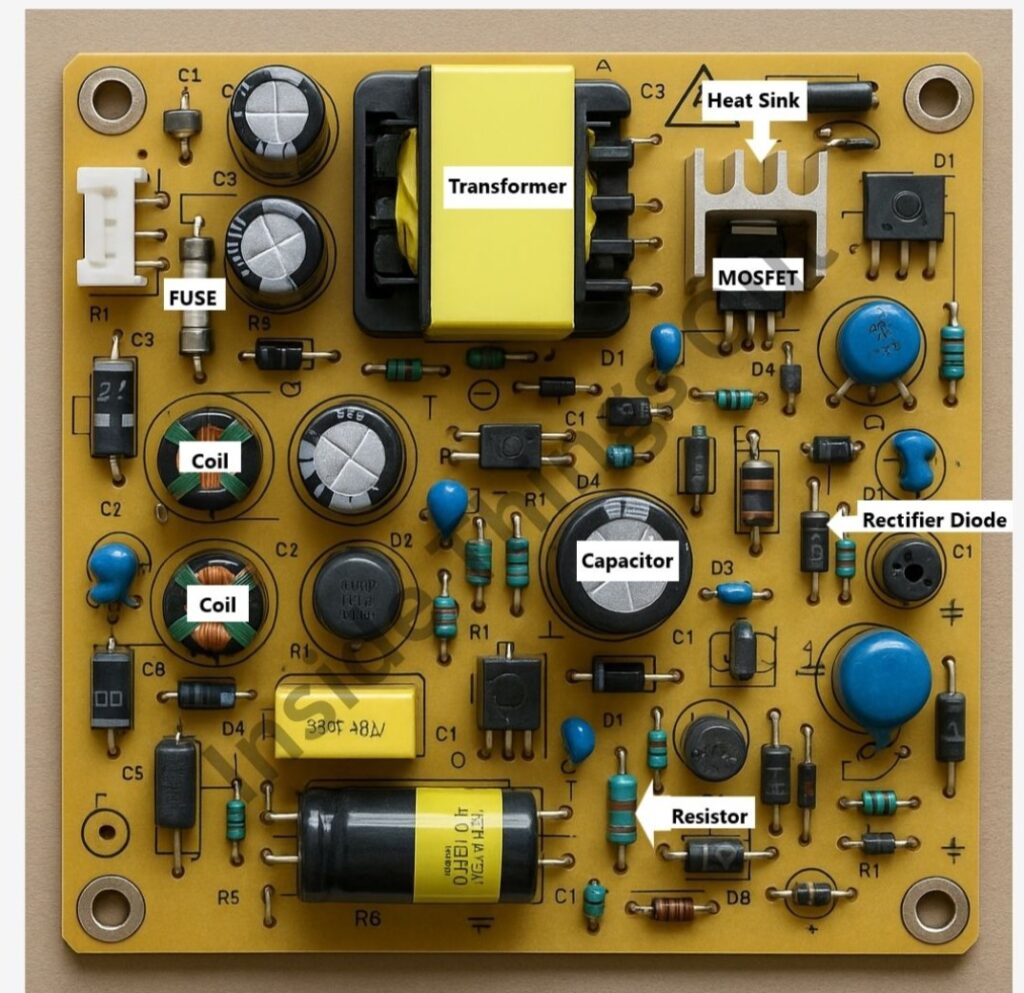
I. Transformer:
● Steps down high-voltage AC to a lower voltage AC.
● Often has multiple windings for different voltage outputs.
II. Rectifier Diodes:
● Convert AC voltage from the transformer to DC voltage.
III.Capacitors:
● Electrolytic Capacitors: Smooth and filter the rectified DC voltage.
● Ceramic Capacitors: Used for high-frequency filtering.
IV. Voltage Regulators:
● Ensure stable output voltage by compensating for variations in input voltage or load.
V. Fuses:
● Protect the board from power surges or short circuits.
VI. Inductors/Chokes:
● Filter high-frequency noise and reduce ripple.
VII. MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors):
● Act as switches in the power conversion process.
VIII. ICs (Integrated Circuits):
● Control power management and switching functions.
IX. Optocouplers:
● Provide electrical isolation between the high-voltage side and low-voltage control circuits.
X. Bridge Rectifier:
● Converts AC input into DC.
XI. Heat Sinks:
● Dissipate heat generated by components like MOSFETs and regulators.
XII. Resistors:
● Control current flow and divide voltage.
➢ Main Board:
The main board is basically the “brains” of your TV and controls everything, from the audio to video streams. All of the user data and settings are also stored on the main board.
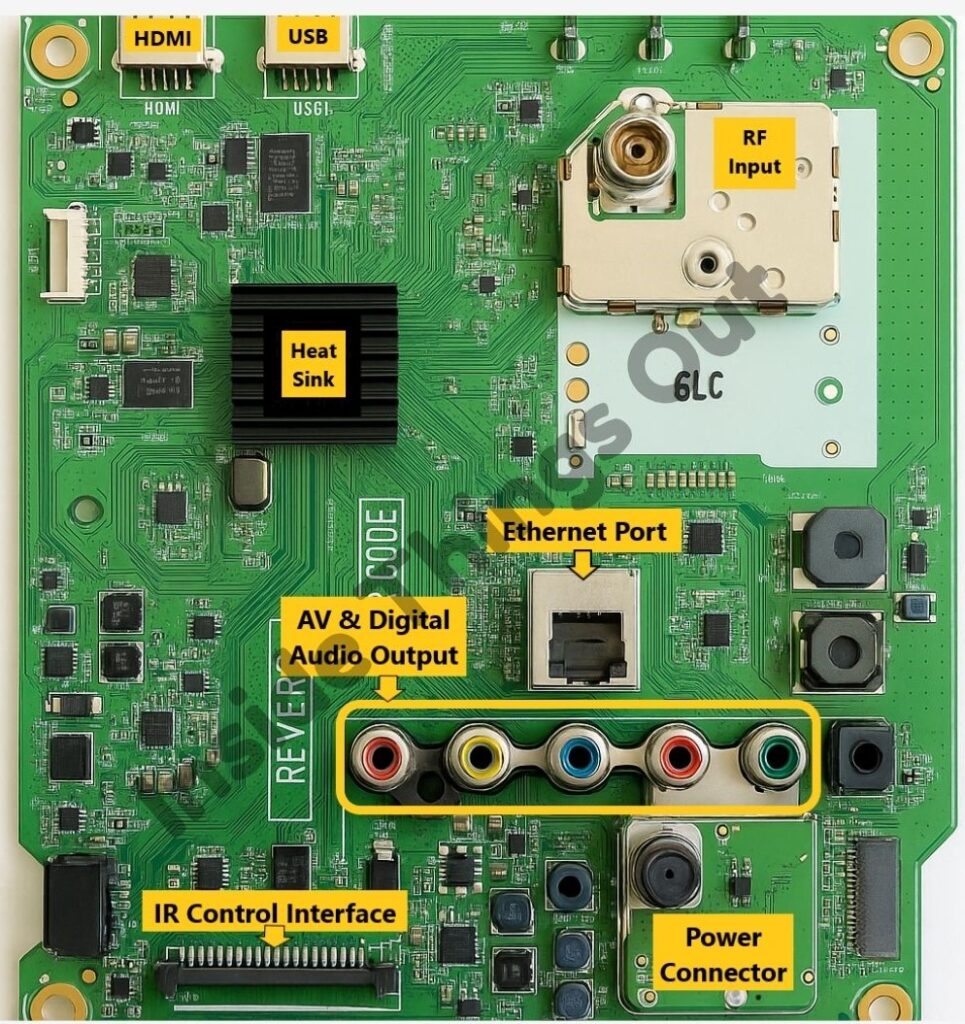
- USB Port (Next to HDMI): USB port for connecting USB drives, external storage, or other peripherals.
- RF Input (Top Center): An antenna or cable input, typically used for receiving terrestrial or cable signals.
- Heat-sink (Left Center): A black heat-sink for cooling the main processing unit or chip underneath.
- Ethernet Port (Middle): Used for wired internet connectivity, often seen in smart TVs for connecting to a local network.
- AV and Component Inputs (Bottom Center): These include the red, green, blue, and yellow RCA jacks for audio and video inputs, allowing for the connection of older devices.
- Digital Audio Output (Near AV Inputs): A coaxial port for transmitting digital audio to external audio systems.
- IR and Control Interface (Bottom Left): A port for connecting an infrared (IR) receiver or control board.
- Power and Other Connectors (Bottom): Includes a power connector and various smaller connectors for signals and control.
➢ Wifi/Bluetooth module:
As you can probably guess, this component helps you connect to your local wifi network and any nearby Bluetooth devices.
➢ IR sensor:
It is short for infrared sensor, and the sole purpose of the IR sensor is to receive the signal from your remote control and send it to the main board as an electronic signal.
➢ LED strips:
Inside the light case (or chassis). LED strips are the light source behind the LCD screen in LED TVs (or CCFL backlit TVs). These strips get their power from the LED driver or the power supply board and control the image brightness on your TV screen.
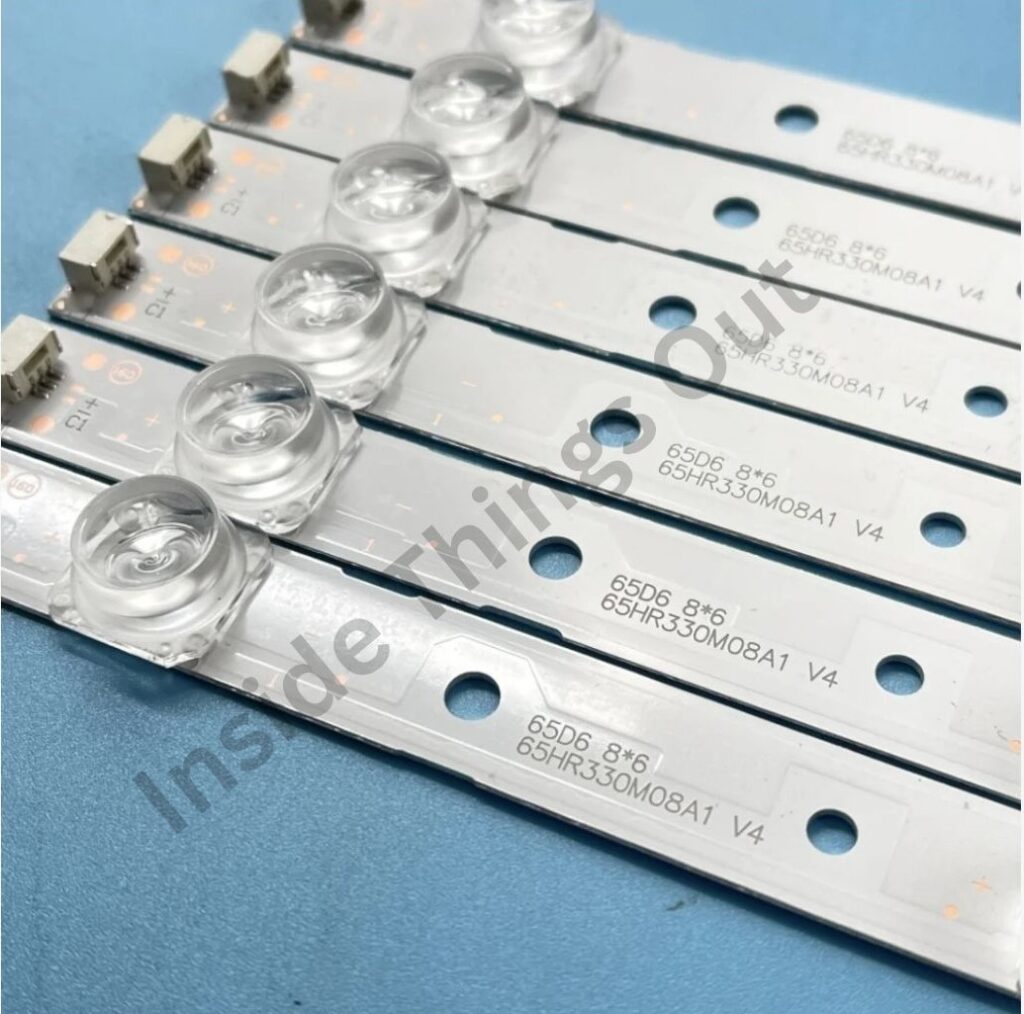

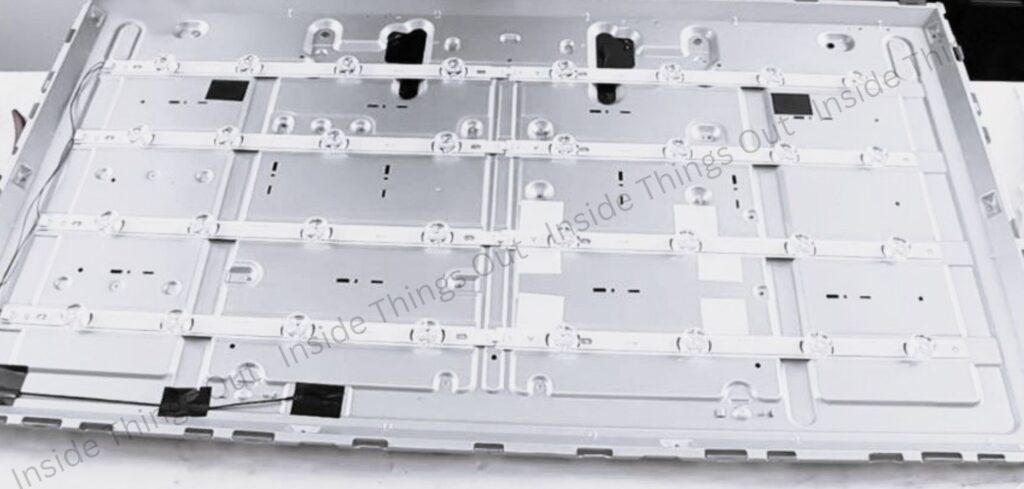
➢ Inverter Board:
For LCD TVs, this part powers the backlight, ensuring the screen is bright enough to view.
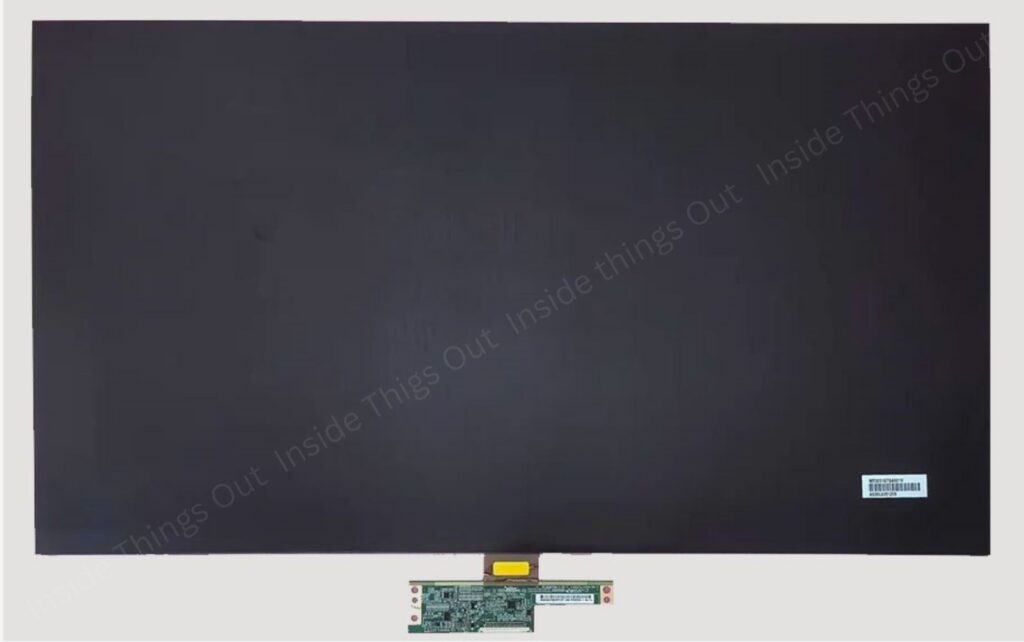
➢ Display Panel:
The screen itself, whether it’s an LCD, LED, or OLED panel, displays the images and video you watch.

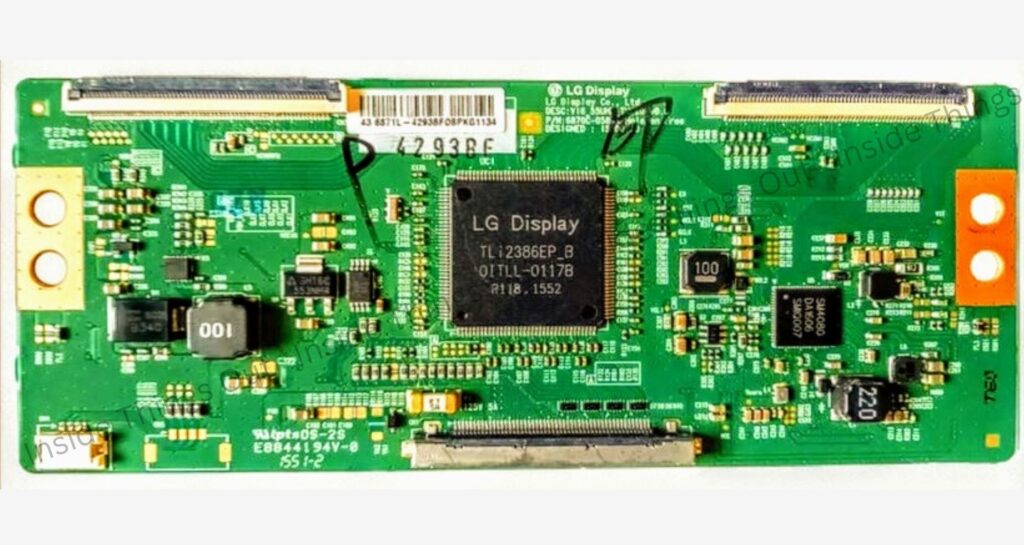
➢ T-Con Board:
Controls the pixelation and refresh rates of the screen, ensuring smooth picture quality.

➢ Speakers:
Deliver the audio you hear from your TV.
Modern TVs have evolved with advanced technology, offering better design, performance, and energy efficiency. Their internal components work together to provide a superior viewing experience, with future innovations promising even more enhanced features.
*****

