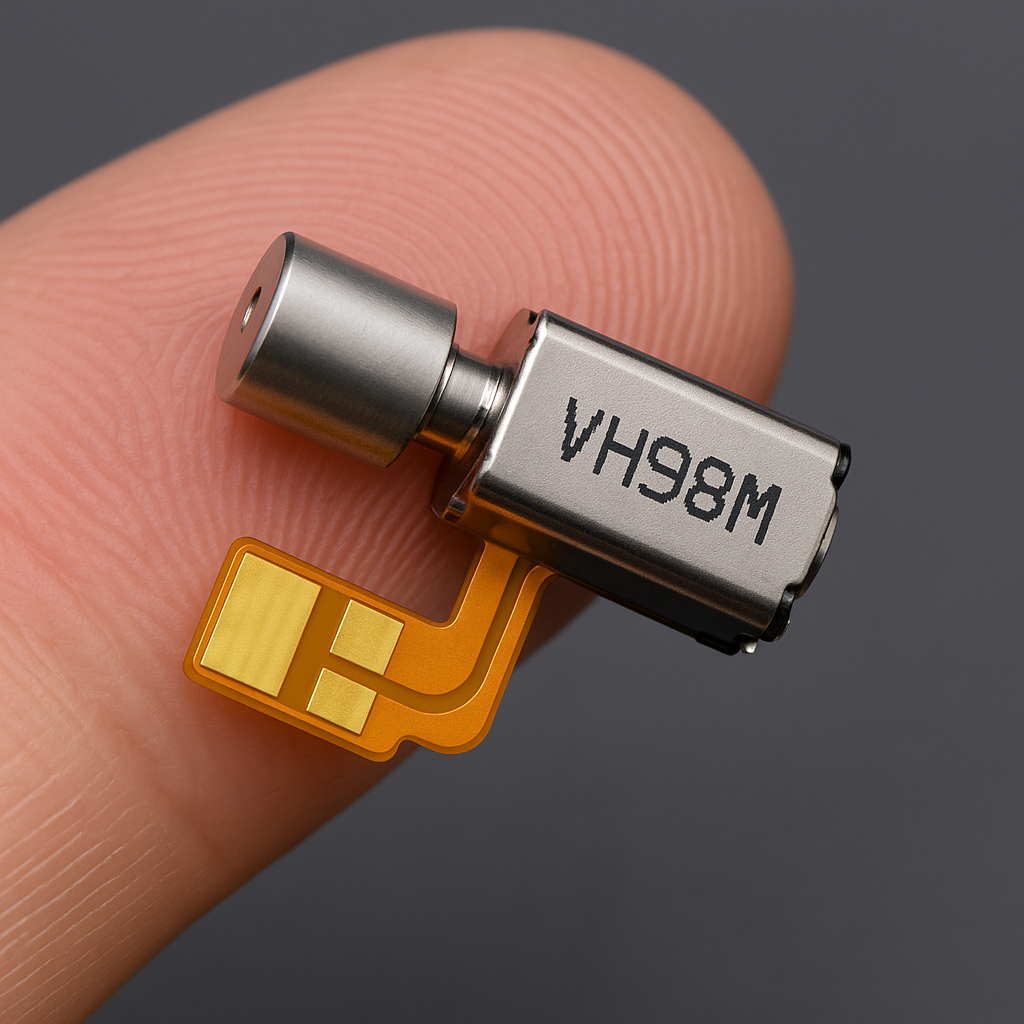
Vibrating alerts on mobile phones were adapted from the first haptic technology used back in the day. Although not present in the first phones, Motorola StarTAC added vibration in 1996 with a technology they called Vibracall. At the time, this was a unique service. Now, mobile phone has a vibration motor which is a small vibrating device that helps the phone alert us without producing noise. What does it contain, and what are its types? Let’s explore below
Types of Mobile Motors
There are two common types:
- ERM (Eccentric Rotating Mass) Motor
- LRA (Linear Resonant Actuator)
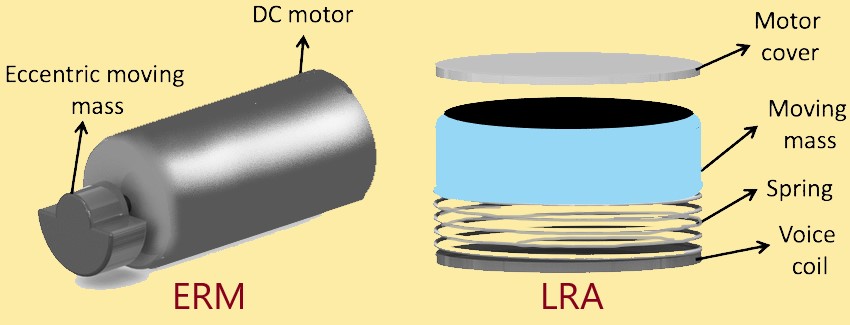
1) ERM Motor (Eccentric Rotating Mass)
The main products and core business of Precision Micro drives have always been ERMs or pager motor Eccentric Rotating Mass vibration motors, also referred to as ERMs. They first became famous when they were used in pagers and as the cell phone industry has developed, they remain very popular in modern phones. A variety of devices and applications now depend on these small vibration motors to provide tactile feedback and messages.
Pager motors rely on miniature Eccentric Rotating Masses, so they commonly go by the name ‘ERM motors’. ERM pager motors produce a vibrating effect through an unbalanced rotation and are beginning to be used for both haptics and vibratory alarms.
It contains various components, such as,
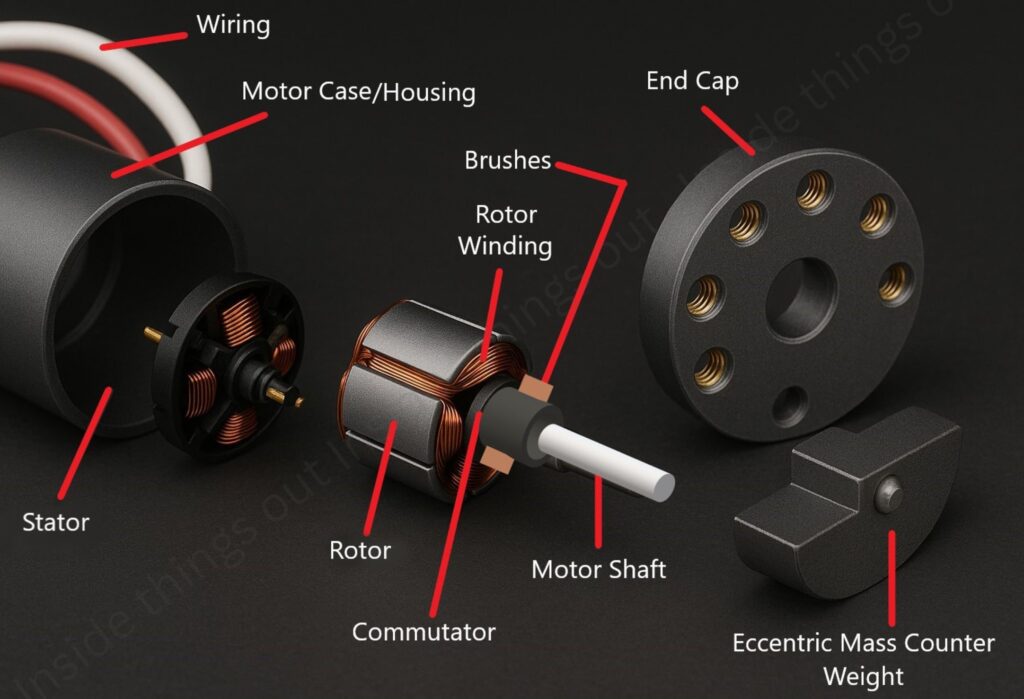

i) Eccentric Weight (Mass):
- A small weight, made of metal or plastic which hangs from a point near the motor’s shaft center.
- It is the spinning that causes the vibration in the disk.
ii) Motor Shaft:
- A central axis links the motor rotor to the outer bearing.
- The eccentric weight fits either by pressing or with glue onto the shaft.
iii) Rotor (Armature):
- The moving part within the stator.
- Includes coils and it is this part that causes the shaft to rotate.
iv) Stator:
- The unchanging piece of the light bulb that produces a magnetic field.
- Assists the commutator by triggering the rotor motions.
v) Commutator:
- A copper ring is fitted and segmented onto the rotor.
- Brings current to the windings by means of brushes.
vi) Brushes:
- Specific brushes that connect to the commutator and take current from it.
- Usually, batteries contain carbon or a similar substance.
vii) Bearings or Bushings:
- Support the shaft and allow it to spin smoothly.
viii) Motor Housing (Casing):
- Houses and helps protect the important components on the inside.
- Most of the time, they are cylindrical and can be made of plastic or metal.
ix) End Caps:
- Covering the motor at the front and rear are removable panels that provide a seal.
- Some cases come with vent holes or mounting points.
x) Wires/Terminals:
- To connect the motor to a form of power.
- Many times, financial statements use different colors to show key details (red for positive, black for negative).
How it works:
A small DC motor spins a weight that’s off-center (eccentric), creating a vibration as it rotates.
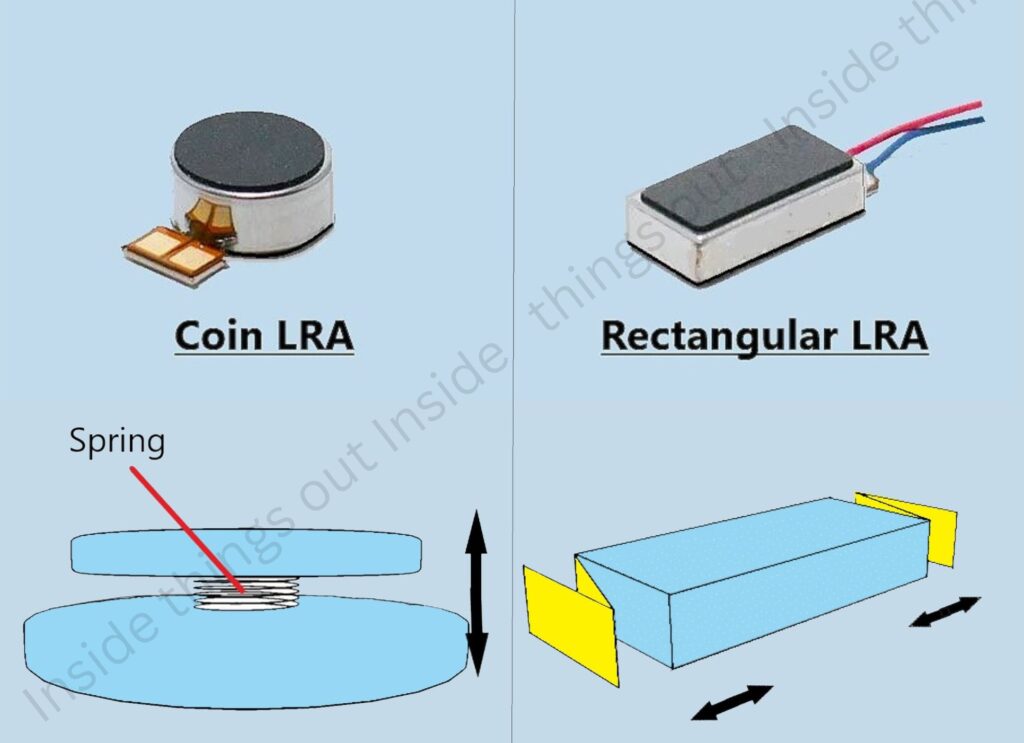
2. LRA (Linear Resonant Actuator)
LRAs give a speedier response and have a longer life than ERMs. So, linear vibration motor (LRA) tends to be used more frequently for handsets, wearable vibration and mobile phone vibration. Besides, linear vibration motors (LRA) vibrate near the same frequency, resulting in much better performance for the haptics functions. Coupling the Vertical direction Vibration and resonance mode through electromagnetic force generated by sine waves.
It has various components such as:
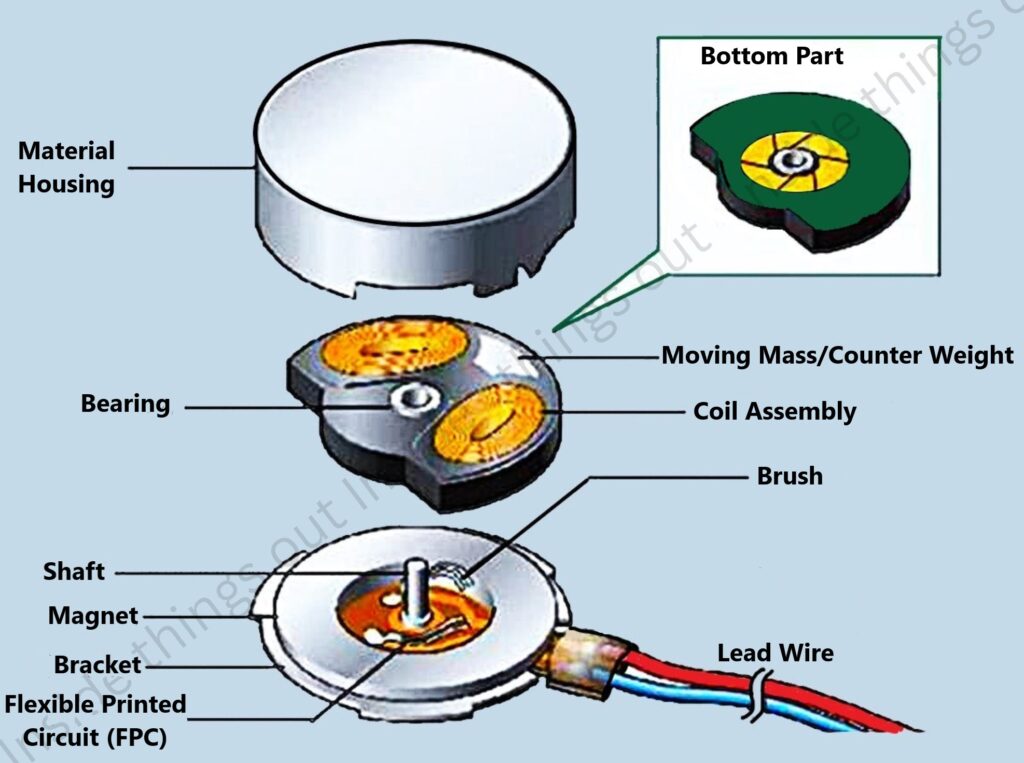
i. Material Housing
- This material sheet is made with strong metal on its exterior.
- Siding and roofing protect the home from weather and damage.
ii. Spring
- It situated at the spot between the back cover and the moving mass.
- Makes the restoring force needed for oscillation.
iii. Moving Mass
- It consists of a central weighted component that oscillates.
- A small motor mounted in the housing, designed to cause vibration.
iv. Coil
- A wire coil made from copper will produce a magnetic field when current is passing through it.
- Built next to the magnet.
v. Magnet
- Makes the coil vibrate with the help of magnetic interaction.
vi. Printed Circuit Board (PCB).
- It supports electronic parts and wire lines inside the cabin.
- The driving circuit connects to the battery by a wire.
vii. Front Housing (Cap).
- The last part of enclosure which seals the cabinet.
- Central posts or shafts are occasionally attached to the moving mass.
How it works:
Uses a spring-mounted magnetic mass that moves back and forth when driven by an AC signal, creating vibration.
3) Piezoelectric Actuators
Another kind of actuator is called a Piezoelectric actuator. An electric voltage is used on these devices to vibrate piezoelectric materials, creating movement. Even so, piezoelectric actuators do not often appear in mobile phones.
Because these actuators can give very precise haptic feedback, they are well-suited for use in devices like those used in medicine. Their high-tech applications have made piezoelectric actuators solid performers in rising markets for wearable items and AR/VR, to the point where ERMs are not practical. However, they are thought to be fragile and often break fairly easily.
In conclusion, the choice between ERM and LRA depends on the specific application’s needs — where cost and simplicity are prioritized, ERMs are suitable; where performance, precision, and user experience are critical, LRAs are the better option.
*****