The earbuds have traveled a long way since their primitive developments of the 1890s when single-ear, huge producing earphones were applied in communicating over the radio and telephones. It all started with the introduction of the Sony Walkman in 1979 which brought lightweight portable earbuds into the media. This trend went on overdrive when apple launched its iPod in 2001 and compact in-ear type headphones became a daily necessity of the music aficionados.
The actual revolution was the 2010s with the emergence of Bluetooth technology, which resulted in the age of wireless earbuds. Introduced in 2016, such products as Apple AirPods showed people a new way of dealing with audio; they provided easy connection, enhanced quality, and intelligent application, such as touch buttons and voice assistant. Earbuds today are not merely listening devices, they are smart, multifunctional, and conveniently made in terms of quality and easy to use.
Earbuds, despite their small size, are made up of several intricate internal components that work together to deliver sound, support connectivity, and enable controls. Here’s a breakdown of the main internal components of earbuds:
1. Speaker Driver (Transducer)
The earbud system has the heart of sound, which is the speaker driver. It operates on the principal of changing the electrical impulses into sound by means of a magnet, coil (know as voice coil) and a diaphragm. There is a magnetic field that is generated when an electrical signal is run through the coil connecting to the permanent magnet inside the earbud. It is through this interaction that vibration of the diaphragm is accomplished and it produces sound which the user hears. They depend highly on the quality and size of the driver and determine factors such as audio output including bass, treble and clarity.
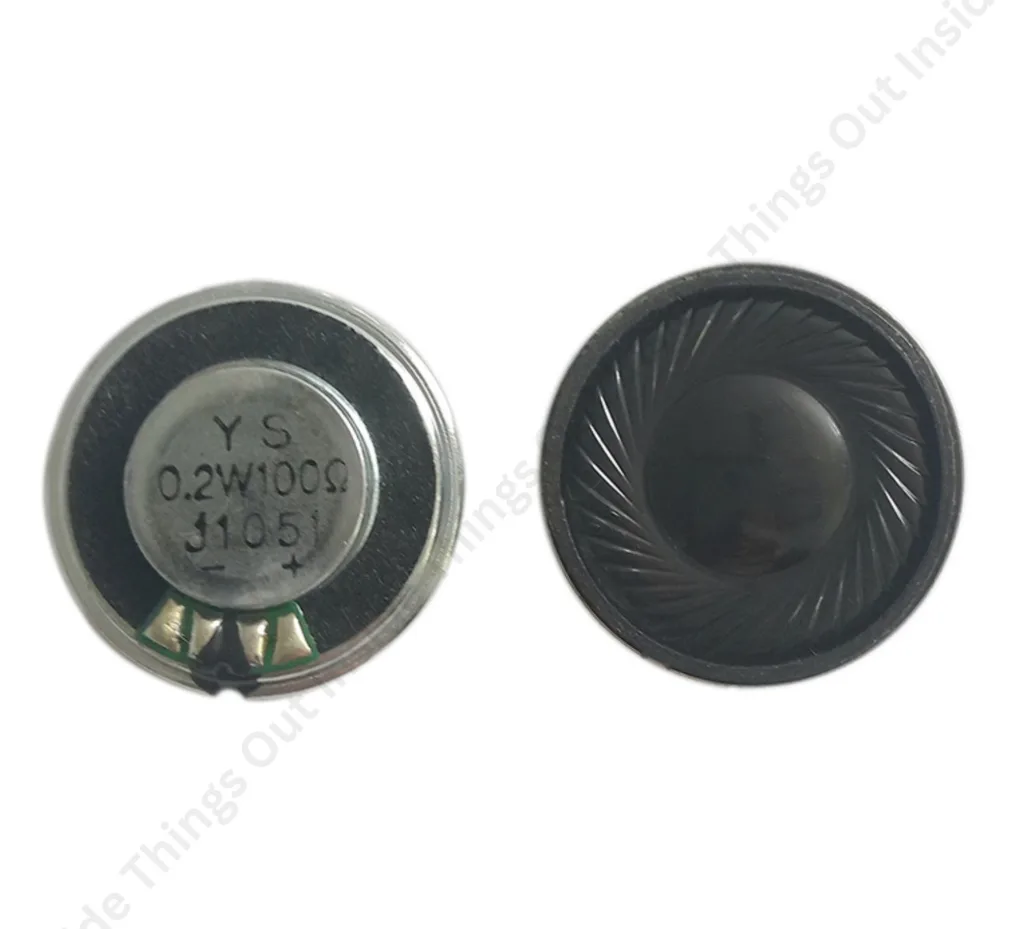

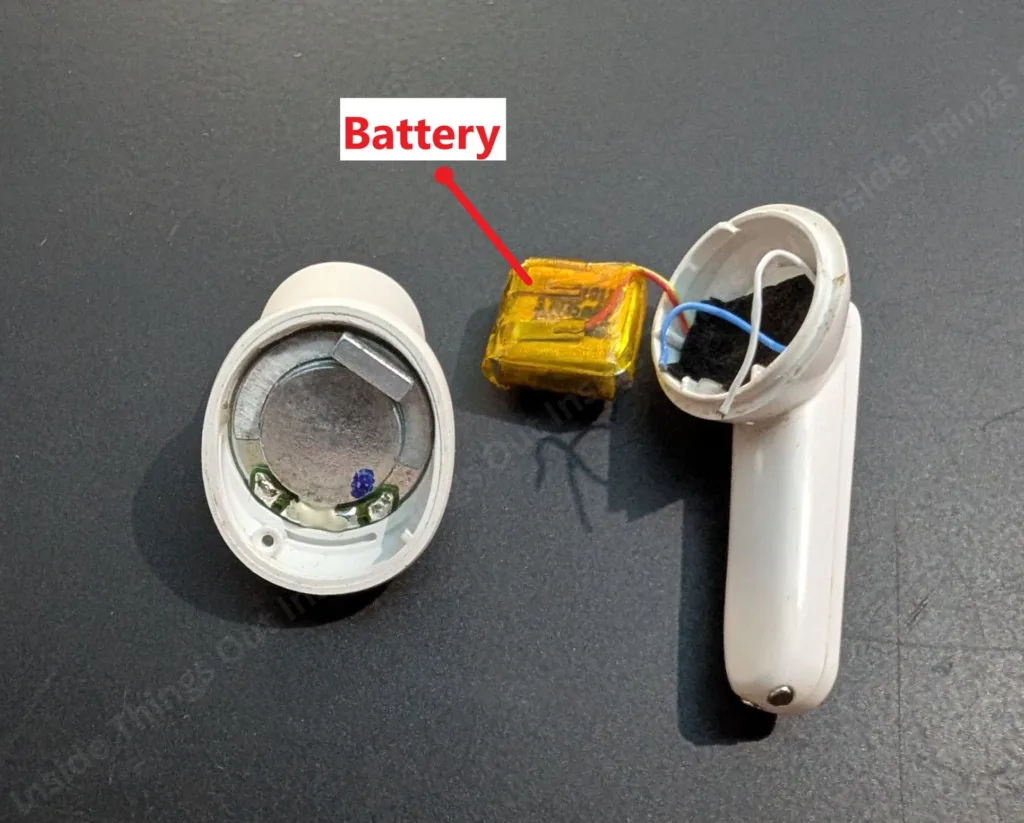
2. Battery
The wireless earbuds have small rechargeable batteries, which may be lithium-polymer or lithium-ion batteries. These batteries are very small and light all the same, yet they give sufficient power to the ear buds at least a couple of hours. The battery powers up every other component and it is charged using a charging case or a cable. Earbud battery size depends upon the model and high-end earbuds usually have power saving options such as automatic off and low power.

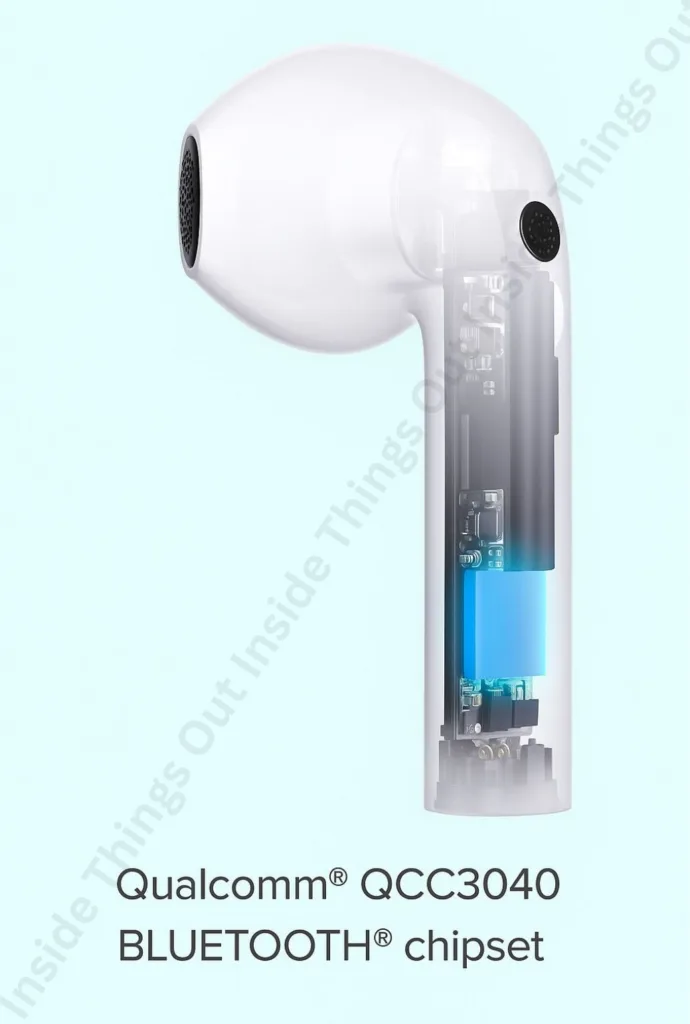
3. Bluetooth Chip/Module
The Bluetooth module is responsible for enabling wireless communication between the earbuds and external devices such as smartphones, tablets, or laptops. This chip handles signal transmission, pairing, audio decoding, and connection stability. In modern earbuds, the Bluetooth chip may also support advanced codecs like AAC, aptX, or LDAC for higher sound quality. It plays a critical role in determining the range and reliability of the wireless connection.

4. Microphone
Earbuds have microphones specially MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) that make it possible to make calls, utilize voice assistants, and benefit various features, such as noise cancellation. Most of the new earbuds contain more than one microphone some to pick up your voice and others to a suppress outside noise. Such mics tend to be small yet sensitive and are coupled up with software algorithms in enhancing clarity, particularly under noisy backgrounds. Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) and Transparency Mode capabilities require microphones.
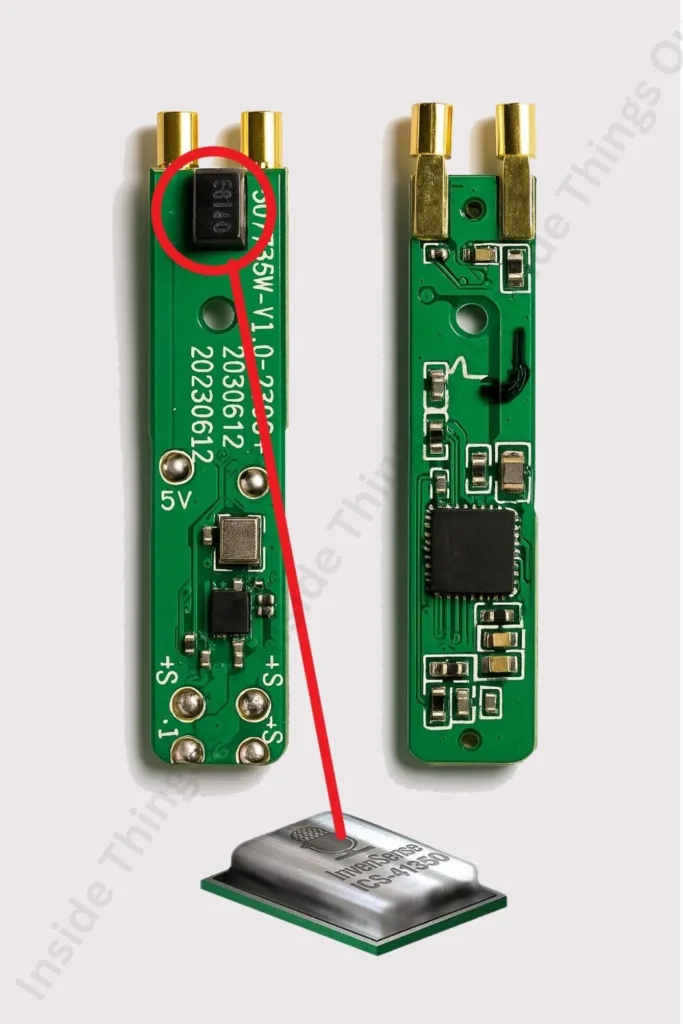
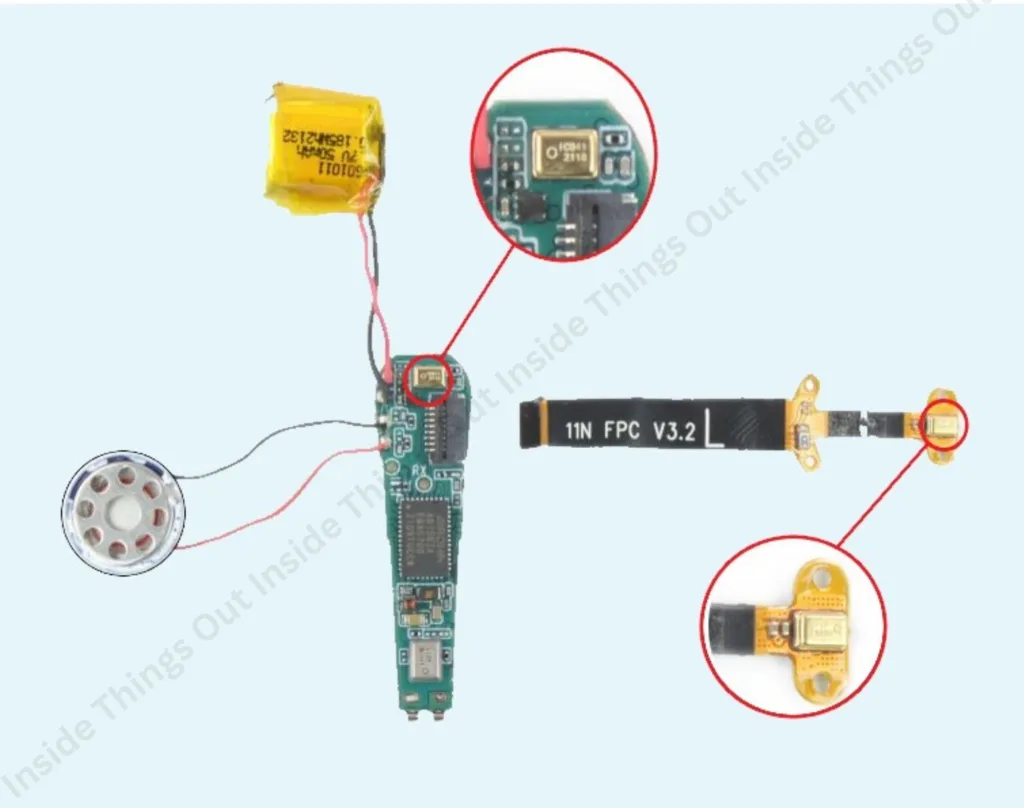
5. Circuit Board (PCB)
The printed circuit board (PCB) is the main point, where all the electronic elements are integrated and joined. It connects the battery, Bluetooth chip, microphones, speaker drivers and control sensors and controls the data and power transfer between those. The PCB must be small, and very efficient and will usually consists of multiple layers so that the circuitry can fit in the small and narrow case of the earbud. It also contains power management and signal processing elements that make it easy to run.

6. Touch or Button Controls
The majority of the latest earbuds include controls that would allow the wearer to play or pause the music, skip the songs, take calls, or use voice assistants. Such controls may be physical buttons or capacitive touch sensors. Touch-sensitive surfaces are activated with a tap or swipe of the fingers whereas buttons have to be physically pressed. The PCB will receive the signals and interpret it before activating the relevant actives that pertain to the control system.
7. Noise Cancellation Components (ANC Models)
Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) earbuds have more microphones and a digital signal processor (DSP) that remains specific to silencing the background noise. These elements act by hoarding external noises and producing reverse sound waves which block the undesired noise before it can move to the ear. It is an adaptive process and can adapt in real-time, so that a user though could have a more immersive and quiet sound experience.
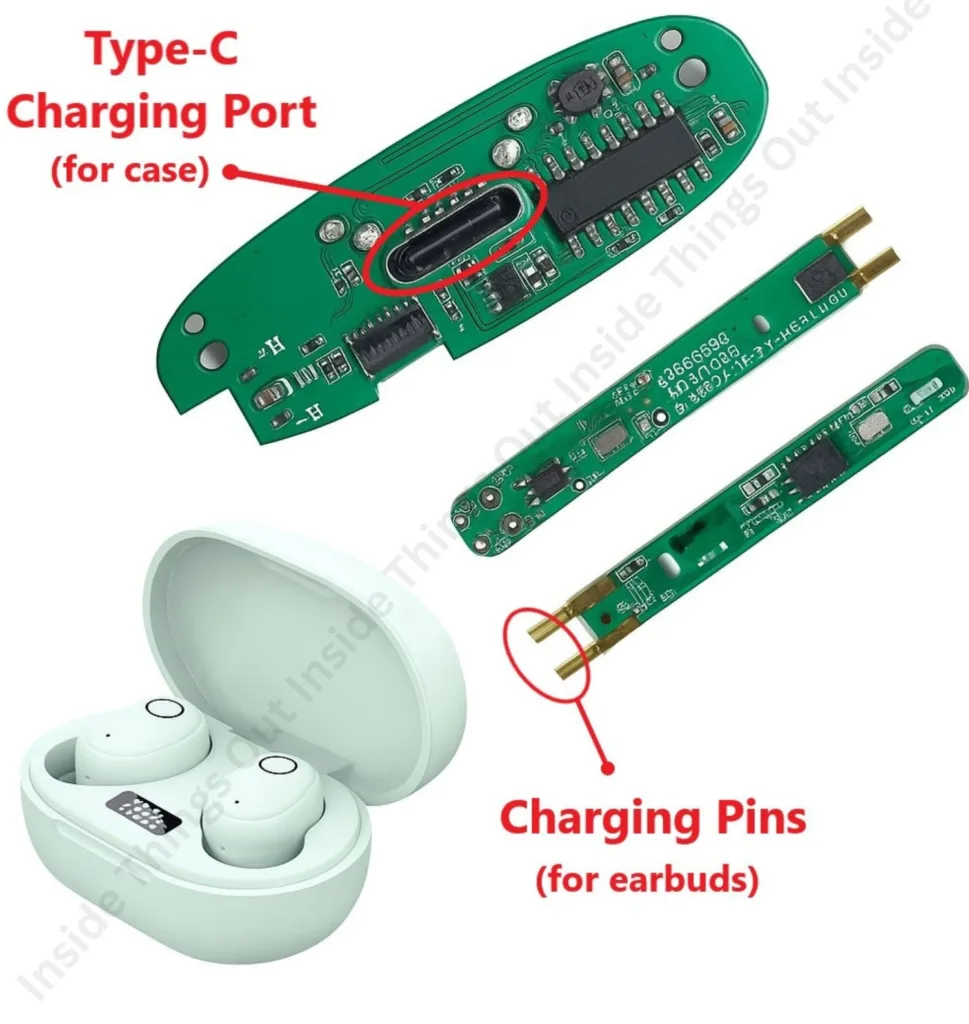
8. Charging Contacts / Port
Small metallic connectors at the bottom of each earbud are known as charging contacts, and they attach to the charging case. When the earbuds are inserted into the case these contacts are connected with pins in the case to provide power to charge an internal battery. Not all of them do necessarily utilize the USB-C port, though they might in case they are not a genuinely wireless system. Charging system is usually provided with safety measures to avoid over charged and heats up.

9. Antenna
The antenna is a simple yet a critical part of the device that allows communication via the Bluetooth medium to be very stable because it transmits and receives the signal. It is normally embedded in the PCB or casted in the case. An efficiently designed antenna provides excellent connection range, minimal signal outages and better general performance, particularly where there is much wireless interference.

10. Optional Sensors and Features
Most high-end earbuds feature optional features such as the proximity sensors, which enable the detection when the earbuds go into the ear or come out. Such sensors can automatically put on pause or resume playing music. Pressure relief vents that improve the comfort inside the ear and the airflow, or LED indicators that tell the battery level, the pairing mode, or whether or not connected can also be found in some of the models.
Although earbuds are tiny, they are the wonders of modern technology with a multiplicity of advanced elements in them. Every component, including the speaker driver, Bluetooth chip, battery, microphones, and touch sensors has a certain contribution to make in providing quality sound, ease of connection, user-friendly convenience and smart features. All these complex internal resources collaborate together in such a way that it provides the performance, convenience, and immersive experience, that the customers demand of the audio device nowadays. The earbuds are more evolved than ever as we are provided with active noise cancellation and biometric measurement; AI-assisted controls and they are more than just an audio instrument; they are wearable smart companions.

