An Aeroplane is a magnificent creation of engineering and it consists of a combination of altogether follow range of essential factors which collectively strive to develop an aeroplane fly under control. On the outside it may appear to be one streamlined machine but within each aeroplane is a well thought out system of parts which are all interconnected with one purpose to guarantee stability, lift, control and safety when it is in the air. Whether it is the massive engines or the sophisticated control surfaces, all the components contribute towards rendering air travelling possible. In this article we would get to see a bit closer about the major systems of an aeroplane and how each of these systems work together in keeping an aeroplane floating in air.
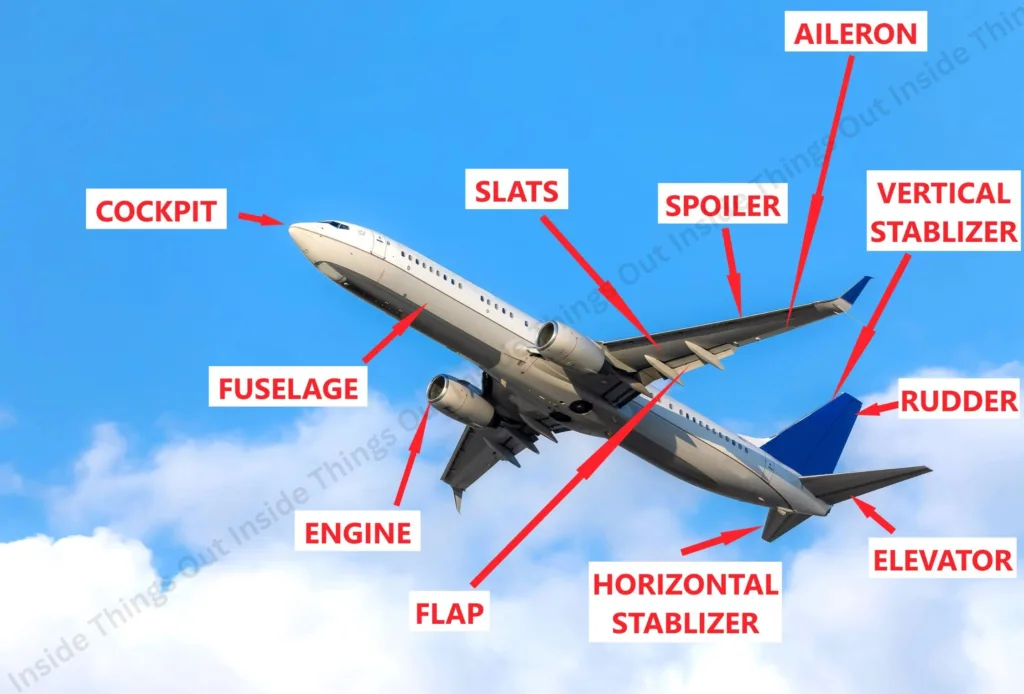

Let’s look at the main components of an air-plane and get a better understanding of their function.
1) FUSELAGE
- An Aeroplane has a main body which is referred to as fuselage. It is the main body where other main subsystems like; the wings, tail assembly and landing gears are mounted.
- The fuselage normally accommodates the cockpit where flight control of the craft is done by the pilot. It also takes the passenger cabin or cargo hold, depending on the type of an aircraft.
- Based on an aerodynamic shape, the fuselage reduces air drag and increases the overall aerodynamic efficiency of the aircraft. It will be made of tough but lightweight material, aluminum alloy, advanced composites or carbon fiber, to make it as strong and as weight effective as possible.
- Moreover, there are vital systems located in the fuselage, such as navigation systems, fuel pipes, power cables, and pressurization systems.
- Being one of the major structural elements, it is important in ensuring that the aircraft structural integrity remains intact when the aircraft is in flight.
2) COCKPIT
The front part of the airplane where airplane pilots control the aircraft is called a cockpit. It also has all the flight controls, navigation and communication facilities in order to fly the aircraft safely. In layman terms, aircraft, it is usually found on the nose (front) of the aircraft.

3) WINGS
Aeroplane wings are important parts that produce lift that enables it to fly above the ground and maintain flight on the air. In this case, here are some of the most important sections and roles of wings:
Main Functions of Wings:
- Make Lift: Wings are designed to cause a pressure difference (airfoil shape) which produces a force-called lift, by lowering pressure on the upper side, and raising pressure on the bottom side.
- Support Control Surfaces: The wings contain ailerons, flaps, spoilers and slats which are used to control the movement of an aircraft.
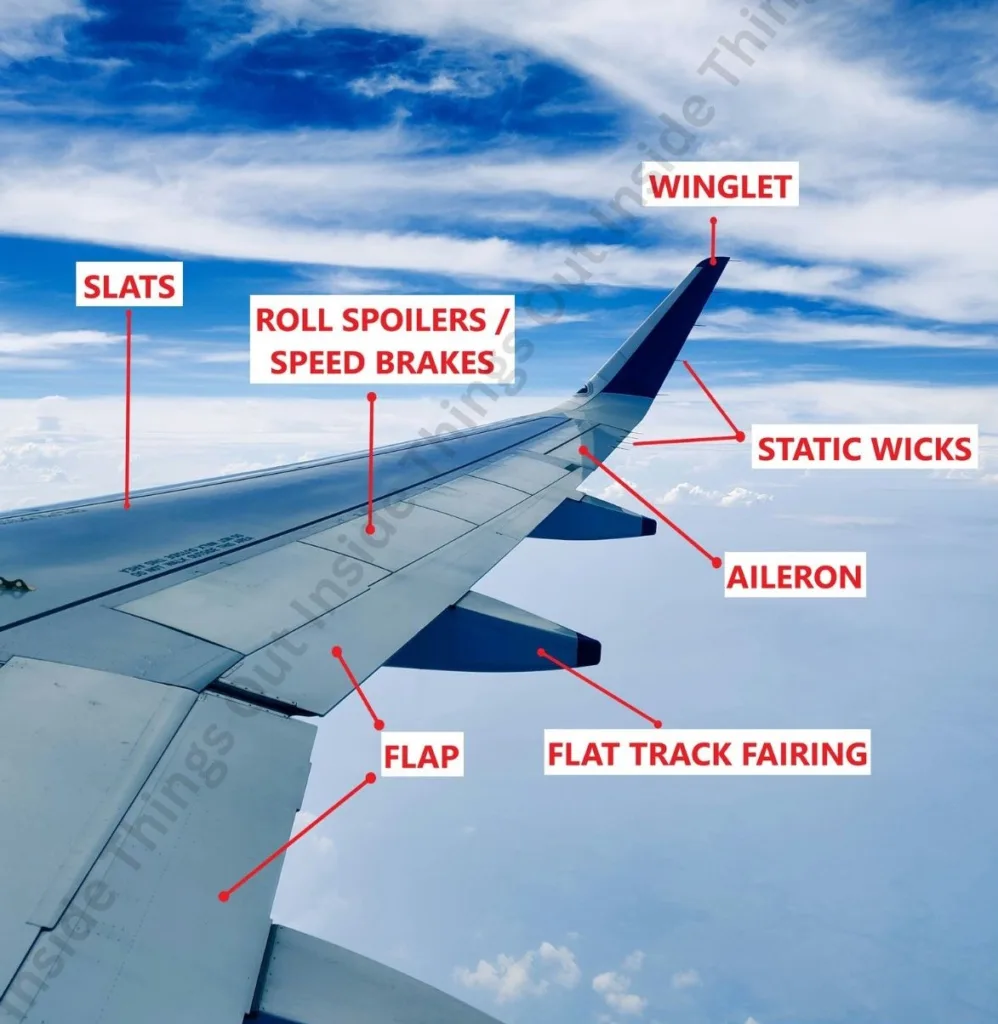

Component Function:
- Ailerons– In or near the wingtips; divert roll (tilting left/right).
- Flaps– Are at a shorter level to the fuselage; add lift and drag; are used during takeoff and landing.
- Slats– Located to the leading edge of the wing; improve the lifting capacity at low speeds.
- Spoilers– On the upper wing surface; decrease the lift and increase the drag, applied during the descent and braking.
- Winglets– They are small vertical pieces off the wing tips; they decrease drag and increase fuel efficiency.
- Flat track fairing (Flap track canoe fairings)- This is an aerodynamic cowling which is featured on certain planes, most commonly on the underside of the wing or the flap assemblies; Decreases air flowing drag, Covers a flap assembly, increases fuel economy.
- Static Wicks– These are the small piece of wire nailed to the back ends of an airplane wings and tails to get rid of both the static electricity.
4) TAIL (EMPENNAGE)
- Gives stability: It maintains the aircraft on straight flight.
- Aids in control: It makes pitch (up/down) and yaw (left/right) control easier to the pilot.
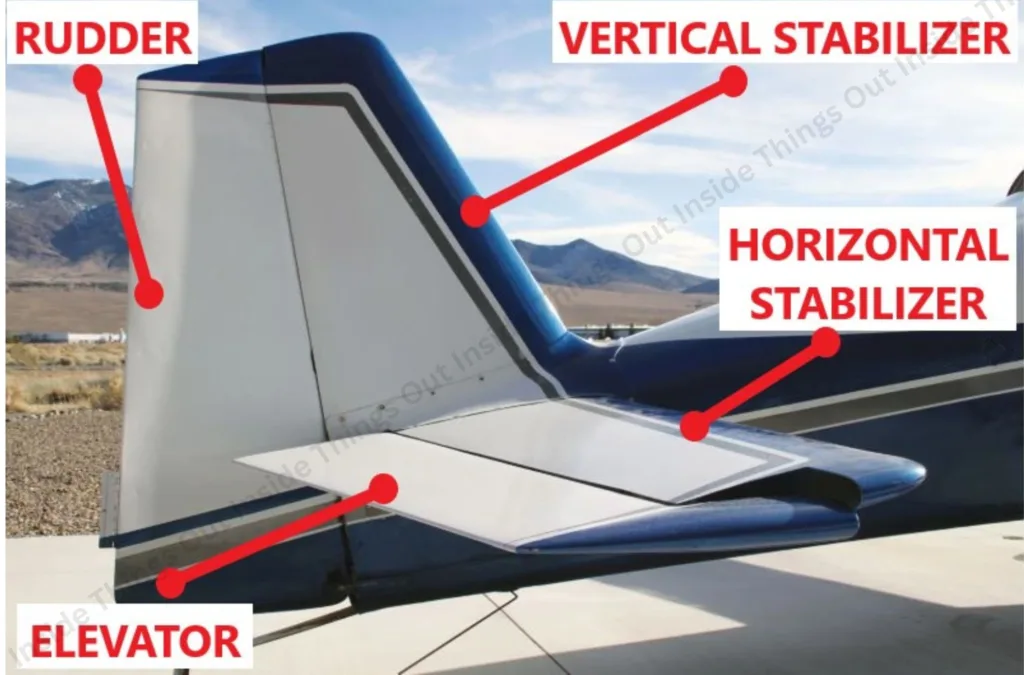
Component Function:
- Horizon Stabilizer– It prevents the up and down the nose pitch; it maintains the aircraft at a horizontal level.
- Elevator-These are flaping control areas at the backside of an airplane, which manage the pitch of the aircraft, thus the angle of attack and the wing lift.
- Vertical Stabilizer (Fin)– It ensures that the nose does not yaw left and right.
- Rudder– It is fastened on the vertical stabilizer; it directs the yaw (lateral motion).
5) ENGINE
Aeroplane engine forms one of the most significant parts of a plane. It is mostly used to make thrust so that the airplane moves forward yet the wings give the force of lift that holds the airplane up.
Types of Engine:
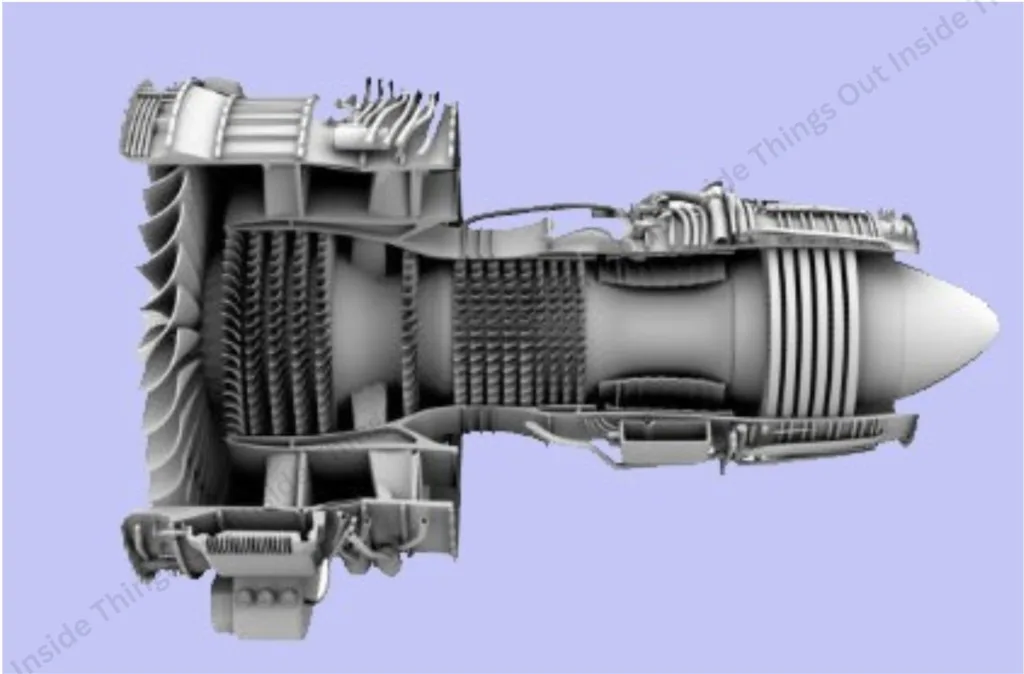
- Turbofan- It is the one mostly used in the modern and contemporary commercial airliners; takes both a fan and a jet style engine to efficiently generate thrust.
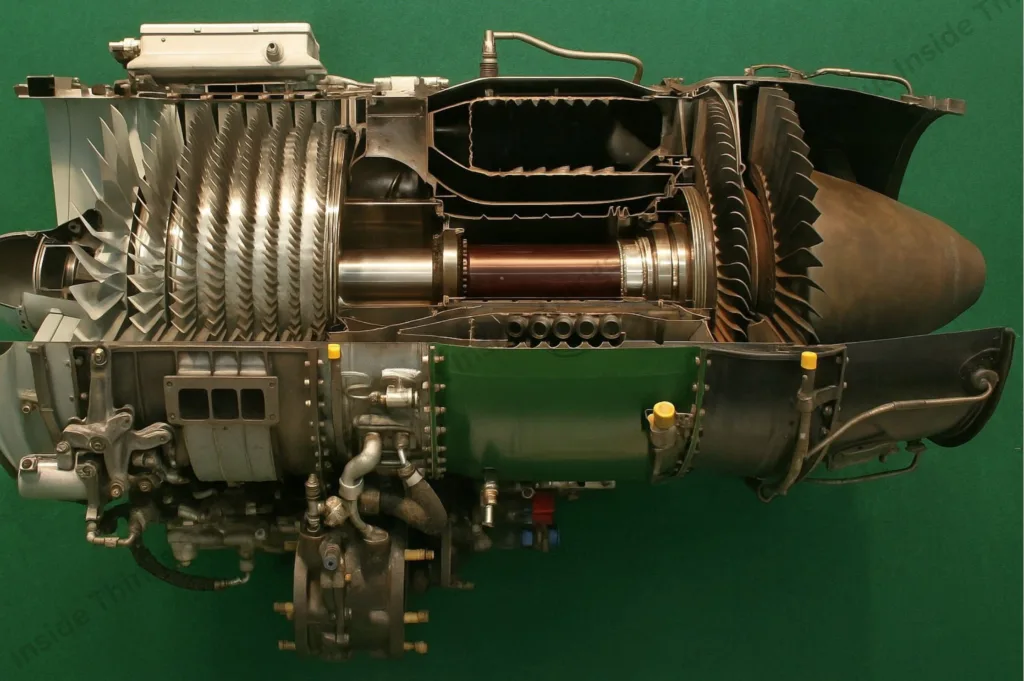
- Turbojet- This is a focus jet that pressurizes the air and combines it with fuel; it is mostly applicable in a military plane.
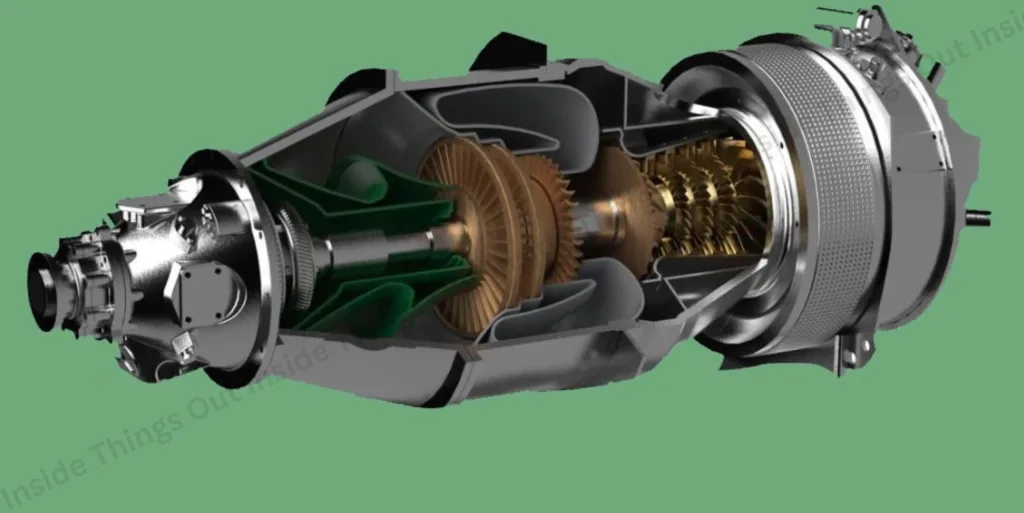
- Turboprop- Turbine- powered through a propeller, efficient in taking shorter flights and at lower speeds.
- Piston Engine- Same as the car engines; they are used in small airplanes.
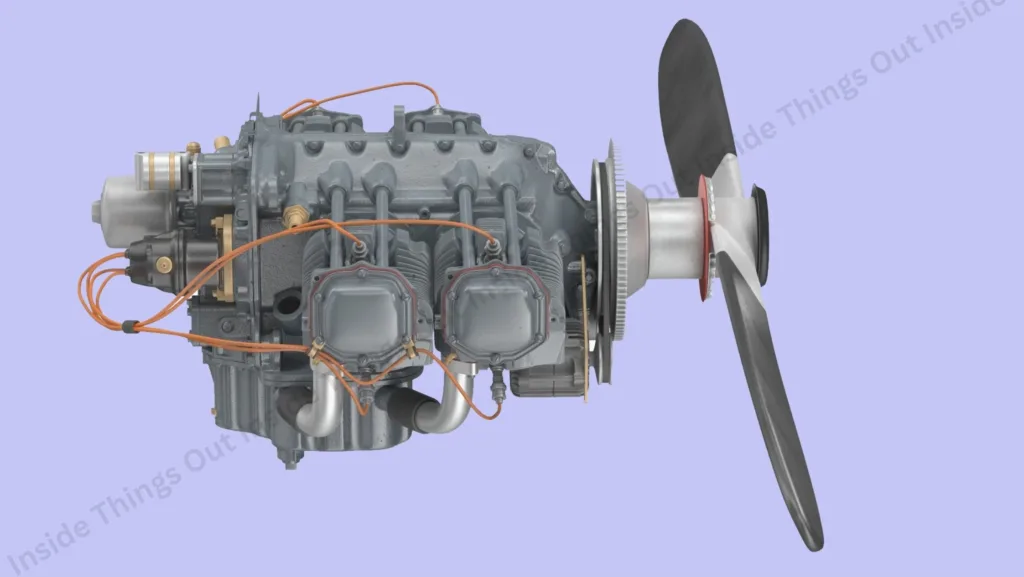
Main parts of an Engine:
- Fan– Draws in large masses of the air.
- Compressor– Pressurizes the in-coming air.
- Combustor– Burns fuel to boil and increase the volume of air.
- Turbine– Derives power in the form of hot gases which propel the compressor and fan.
- Nozzle– Vents gases in high velocity, to generate thrust.
6) PROPELLER
A propeller is a piece of aircraft engine that is meant to convert the rotational force into thrust or pulling or pushing the plane through the air.
How a Propeller Works:
- It is made up of blades which are hinged to a hub.
- The blades in the shape of the airfoil cut through the air as the propeller is being rotated by the engine.
- This induces a pressure difference, which pushes the forward thrust (same as a wing induces the lift phenomena).
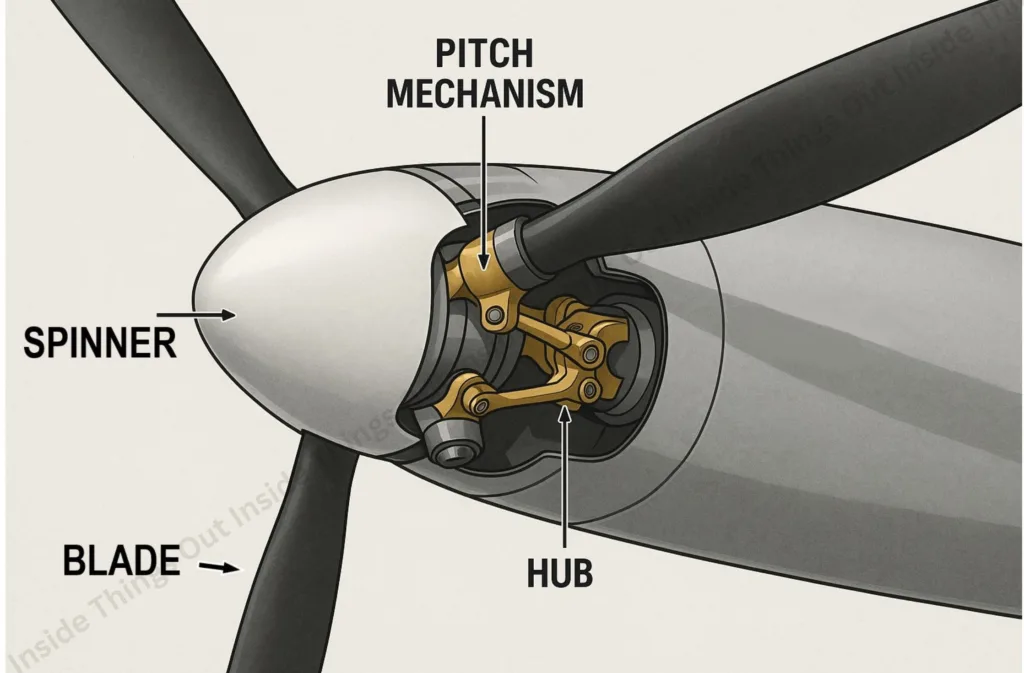
Key Parts of a Propeller:
- Blades– The revolving airfoils which generate thrust.
- Hub– The center of blade attachment to engine shaft.
- Spinner– Shortened cover that gives low drag and shields the hub.
- Pitch Mechanism– Sets blade angle to suit varying flight condition (in variable-pitch props).
7) LANDING GEAR
Landing Gear are the undercarriages of the aircraft which hold it, on landing or on the ground and when taking off. So here goes a brief rundown:
Main Functions:
- Help to carry the weight of the aircraft on the ground operations.
- Shock absorbing in landing.
- Offer brake and steer (nose/tail gear in particular).
- The retracting and extending reduces drag in flight.
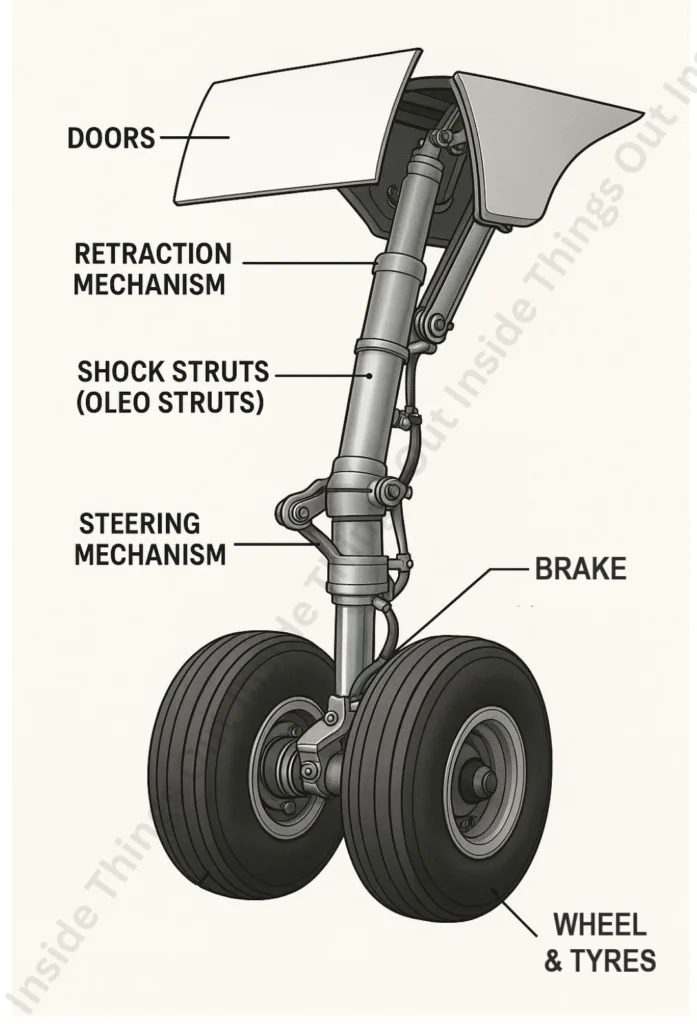
Key Components:
- Shock Struts (Oleo Struts): Dampens impact at landing.
- Wheels and tires
- Brakes: Normally on main wheels.
- Steering Mechanism: At the nose/tail wheel usually.
- Retraction Mechanism: Hydraulic, or electric.
- Doors: Cover when the gear is retracted.
Conclusion
Aeroplane is not just a flying machine; it is an ingenious assembly of well thought out components, each with its designated task to perform. The wings that propel it, the engines that propel it, the tail that stabilizes it, everything in it synchronizes to take it up in the skies to fly securely and comfortably. The next time you see a plane flying over, you will remember that this is no longer just metal with engines, but a well-organised system that has its structure and everything is there for some reason
If you have any questions, or comments, or corrections, please let me know below.
Thanks for reading!

